Cold plates and scorching melts: New knowledge on historical past of Pacific Ring of Fire
About 2000 kilometers east of the Philippine Islands lies probably the most well-known topographical peculiarities of the oceans: the Mariana trench. Reaching depths of as much as eleven,000 meters under sea degree, it holds the document because the deepest level of the world’s ocean. This 4000-kilometer-lengthy trench extends from the Mariana Islands within the south by way of the Izu-Bonin Islands to Japan within the north. Here, the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Philippine Sea Plate, leading to intense volcanic exercise and a excessive variety of earthquakes. The complete space is a part of the “Pacific Ring of Fire.”
But when and the way precisely did the subduction of the Pacific Plate start? This is a controversial matter amongst scientists. An worldwide workforce led by the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel, the Japan Agency for Marine Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) and the Australian National University investigated this early part of subduction alongside the Izu-Bonin-Mariana trench, with findings revealed within the March version of the scientific journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
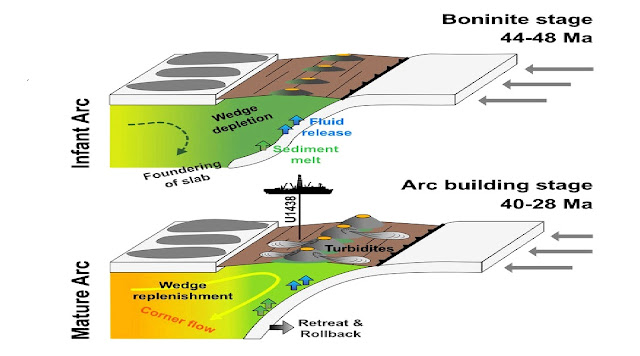
The research is predicated on a drill core that was obtained by the International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) in 2014 with the US analysis drilling vessel JOIDES RESOLUTION some 600 kilometers west of the present Izu-Bonin Trench. “For the primary time, we have been capable of get hold of samples of rocks that originate from the primary levels of subduction,” says Dr. Philipp Brandl from GEOMAR, first writer of the research. “It is understood that the lively subduction zone has been shifting eastwards all through its historical past and has left necessary geological traces on the seabed throughout its migration. We have now drilled the place the method has begun.”
The group of the JOIDES RESOLUTION was capable of drill greater than 1600 meters deep on the seabed, beginning at a water depth of round 4700 meters under sea degree. “This is already on the restrict of the technically possible,” emphasizes Dr. Brandl. Based on evaluation of this drill core, the researchers have been capable of hint the historical past of the subduction zone layer by layer as much as the roughly 50 million yr-previous rocks on the backside of the core, that are typical for the delivery of a subduction zone. “There has not been such an entire overview but,” says Dr. Brandl.
Brandl and his colleagues have been now capable of purchase and analyze microscopic inclusions of cooled magma from the rocks. The knowledge obtained present the scientists with insights into the historical past of volcanic exercise on the Pacific Ring of Fire 30-forty million years in the past. The researchers discovered proof that volcanism was solely starting to realize momentum. The volcanic exercise intensified with the rollback of the subduction zone in the direction of the east and the large explosive stratovolcanoes shaped, just like these current these days, for instance alongside the western rim of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
However, additional drilling is important to check the validity of those observations. “The extra drill cores we will achieve from such previous strata, the higher we study to know our personal planet,” Dr. Brandl says. The query of how subduction zones develop just isn’t solely fascinating to know the historical past of the earth. Subduction zones are the drivers for the chemical change between the earth’s floor and the earth’s inside. “The dynamics of a subduction zone can thus additionally affect the velocity of worldwide elemental cycles,” summarizes Dr. Brandl.
The above publish is reprinted from Materials offered by Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR).